The Nutritional Benefits of Irish Cheddar Cheese
Recent findings suggest that Europeans have been producing and consuming cheese since at least the 6th millennium BC1. Cheddar Cheese is a food that can cause consumer confusion when it comes to understanding its role in a healthy diet. Despite the nutritional value of cheddar cheese it can often be perceived as unhealthy. The fact that cheese contains saturated fat and salt cannot be ignored. Saturated fat and salt in isolation can be linked to negative health impacts such as cardiovascular disease but when consumed together cheese’s total nutritional package is associated with positive health effects.
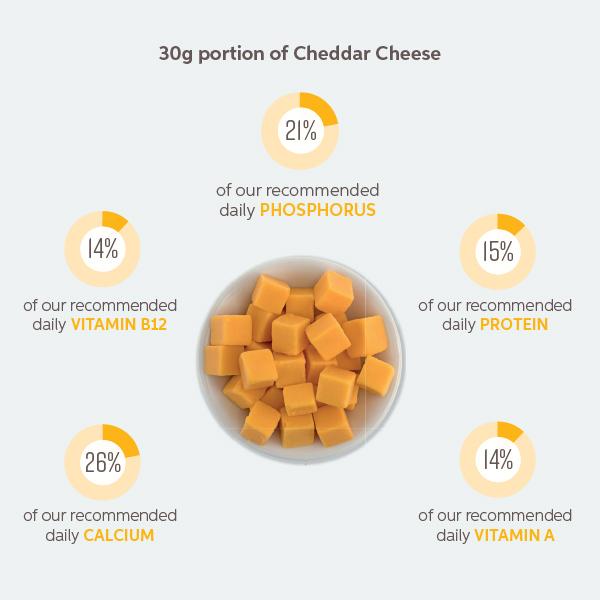
Cheese is a matrix of nutrients. A 30g portion of cheddar provides calcium, phosphorus, vitamin B12 and protein and can be enjoyed as part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Dairy, more than the sum of its parts
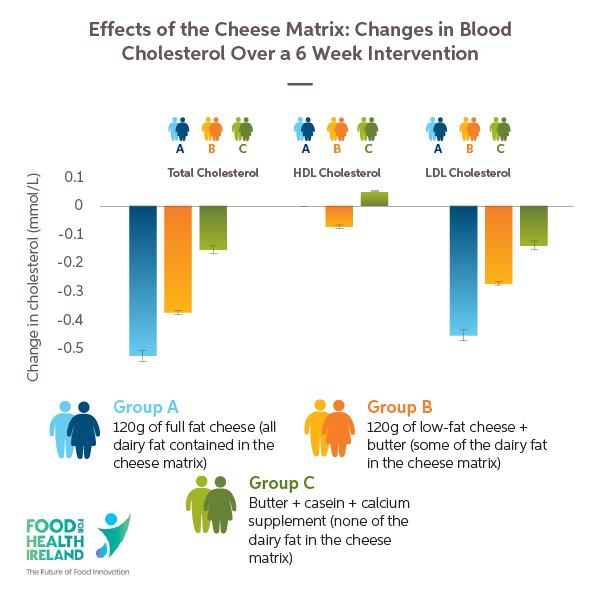
Food for Health Ireland (FHI) is an Enterprise Ireland technology dairy centre. Research by FHI examined the relationships between the cheese matrix and heart health using Irish cheddar cheese6. At the end of the 6 weeks study, individuals in Group A had significantly lower total and LDL-cholesterol than group C, even though they all consumed the same amounts of fat, protein and calcium. There was no changes in other measurements such as HDL-cholesterol, body weight or body fat. The results of the study indicate that dairy fat consumed as cheese affected blood cholesterol differently. This effect appears to be due to an additive effect of the nutrients contained within the structure of cheese compared to when these nutrients are consumed separately.
This indicates the importance of the dairy matrix, where instead of examining single nutrients in isolation, the benefits of the unique combination of nutrients interacting within a food are considered5.

It has been suggested that the effect on LDL cholesterol may arise from the relatively high levels of calcium and protein found in cheddar cheese. These nutrients may counteract the cholesterol raising properties of saturated fat by binding to the fat and preventing absorption, but more research is required7.

Do dairy products from grass fed cows contain additional benefits?
Research on Irish cheddar cheese has found that grass-fed dairy has several nutritional benefits compared to thatfrom grain-fed cheese8.
Higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to non-grass-fed cheese.Twice the levels of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in grass-fed cheddar compared to grain-fed.Higher levels of beta-carotene. Beta-carotene also gives Irish cheddar and butter its golden hue.