Boosting Immune Health
Dairy contains key nutrients which may influence the immune system
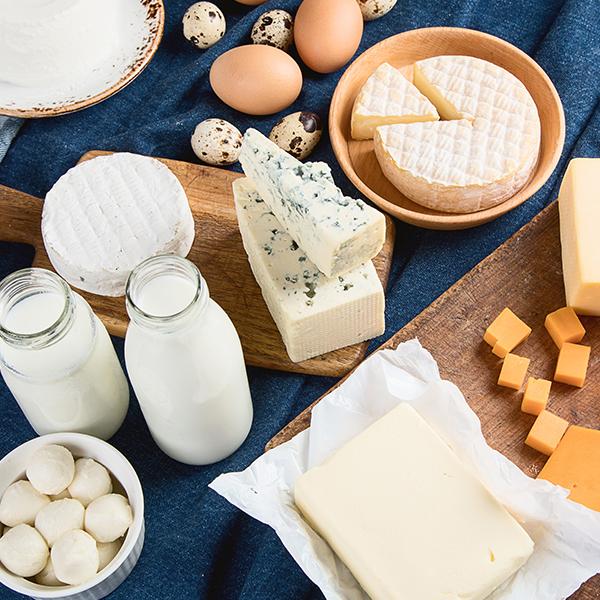

Dairy is a unique blend of nutrients that may include calcium, phosphorus, iodine, Vitamin B2 and B12, fermented cultures (yoghurt and cheese), bioactive peptides and high-quality protein containing all of the essential amino acids.
‘The Dairy Matrix’ hypothesis suggests that the nutrients in dairy can interact with one another in ways that are beneficial for health. This also includes some of the nutrients that support the immune system, such as vitamin B12 and folate, found in milk, cheese and yoghurt, and vitamin A and zinc specifically for hard cheeses like cheddar.

It is well established that nutrition plays a key role in supporting the health of the immune system.
Nutrients can be divided into 2 categories: macronutrients, and micronutrients. Macronutrients are those nutrients that the body needs in large amounts. These provide the body with energy (calories). Micronutrients are those nutrients that the body needs in smaller amounts.
Protein
Milk naturally contains 3.5% protein (80% casein, 20% whey).Protein plays an important role in the immune response in that it provides amino acids and energy to make immune cells and other immune factors or components.
Dairy proteins are complete protein sources, meaning that they contain all essential amino acids. These are nutrients that the human body cannot make, so are required to be sourced from the diet.

Dairy protein is also a rich source of bioactive components:
Lactoferrin- is one of the largest proteins found in milk. Lactoferrin has many roles in the body including having strong antioxidant, antibacterial and antiviral properties which can provide protection against certain fungal, viral or bacterial infections.
ɑ-lactalbumin- is a natural whey protein containing a naturally high content of all essential and branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), making it a unique protein source. It may play a role in the infant gut development and therefore on the immune system.
Immunoglobulins (Ig)- are antibodies that are created in the body in response to antigenic or immunogenic stimuli such as bacteria and viruses, and thus provide protection against microbial infections.







